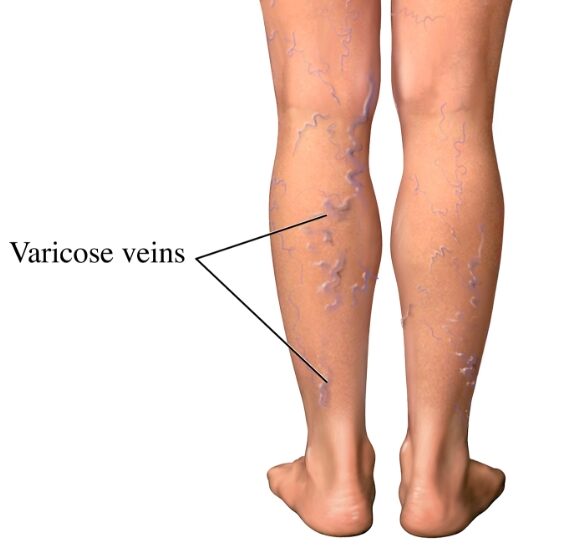
At HeptaCare Health, we specialize in advanced varicose vein treatments, offering safe, effective, and non-surgical solutions like EVLT. Our expert medical team ensures personalized care, helping patients regain confidence and mobility with minimal downtime.
With state-of-the-art laser technology, we focus on providing pain-free, lasting relief from varicose veins. Whether you’re experiencing leg pain, swelling, or visible veins, we’re here to help you achieve healthy, beautiful legs.
Happy Patients
Disease
Hospitals
Cities
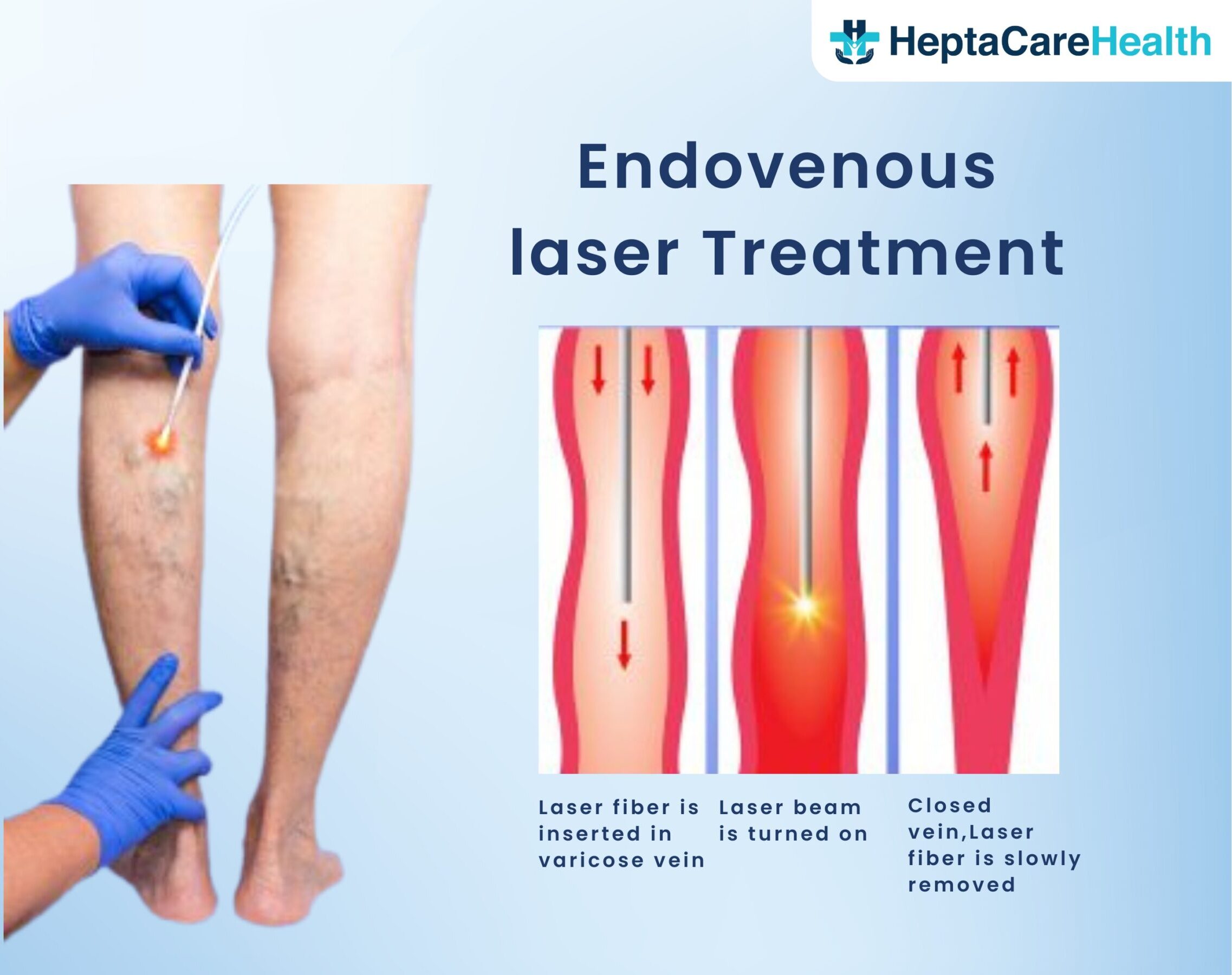
Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT) is a minimally invasive procedure for treating varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency. It uses laser energy to seal off damaged veins, improving circulation and relieving symptoms such as pain, swelling, and discomfort.
If you have painful, bulging, or swollen varicose veins, EVLT could be the perfect solution. Schedule a consultation with our experts today!
Varicose veins are a common clinical problem in vascular surgery that may significantly affect quality of life, with involvement as high as 10% to 40% of the population in China. However, different treatment methods have different results.1 In 1997, Bergan first applied endovenous laser treatment (EVLT) for varicose veins, which has been applied in China since 2003. EVLT is safe and effective,2 4 especially regarding faster recovery.5 However, the performance standards for this technique have not been released to date. Consequently, inappropriate EVLT procedures increase the incidence of postoperative complications or even undermine the apparent advantage of this technique in terms of fast patient recovery. Nevertheless, it has been extensively applied in basic hospitals. Since 2011, we have explored and improved the technique to reduce postoperative complications based on the considerable work experience of others.
EVLT has become a widely accepted method for treating varicose veins, particularly involving the great saphenous vein (GSV). Research suggests that while different techniques yield varied outcomes, EVLT is at least as effective as traditional surgery in managing GSV varicosities. Primary failure and recurrence rates of EVLT are comparable to those of surgical interventions. Despite utilizing higher energy levels, EVLT has not demonstrated an increase in complication rates, making it a safe and effective option.
Varicose veins typically result from venous hypertension in the lower extremities due to congenital valve incompetence, weakened vein walls, or prolonged standing. The conventional surgical approach includes high ligation and stripping of the GSV at the saphenofemoral junction (SFJ), with or without phlebectomy. This procedure involves cutting and tying the GSV and its tributaries, stripping the GSV trunk, and removing other varicose veins. The goal of all surgical methods is to relieve venous hypertension and prevent recurrence by eliminating the source of reflux.
While EVLT alone has shown effective symptom relief for superficial venous insufficiency, incomplete removal of the GSV remains a leading cause of recurrence. To address this, EVLT combined with high ligation has been explored. High ligation serves two purposes:
Prevention of Deep Vein Damage: By securing the GSV at the SFJ, the laser fibre is prevented from advancing into deeper veins.
Thrombus Migration Control: It minimizes the risk of thrombus traveling from superficial to deep veins, thereby reducing the chance of pulmonary embolism.
Though recanalization has been reported following standalone EVLT, such cases have not been observed at our center using B-ultrasound. However, long-term clinical and duplex ultrasound follow-up is essential.
Saphenofemoral recurrences often result from anatomical variations such as double GSVs or incomplete high ligation. Addressing these through high ligation and tributary dissection, including tangential repair of the femoral vein, helps eliminate vortex formation at the SFJ and reduces recurrence rates.
Studies show similar recurrence rates in EVLT with and without high ligation. However, while the non-ligation group had less neovascularization, it experienced more incompetent tributaries and earlier recanalization at five years, indicating a potential long-term benefit of incorporating high ligation.
EVLT uses high-energy lasers, with heat absorbed by hemoglobin and surrounding tissues. This creates steam bubbles that cause blood to boil and damage the endothelium and intima, leading to vein wall thrombosis, fibrosis, and eventual closure. Histologically, EVLT affects the endothelial and intimal layers, internal elastic lamina, and part of the media.
The GSV is deeper in the thigh, so skin burns are rare. However, calf varicosities are more superficial, increasing the risk of thermal injury. Methods to prevent burns include:
Injecting Protective Solution or Using a Pump: Complicated but effective.
Spraying Saline: Our preferred method involves spraying saline directly on the skin overlying the laser path to reduce temperature. This is simple, effective, and minimizes burns.
Laser Technique Modifications: Using intermittent rather than continuous laser emission, or increasing fibre movement speed, can help reduce energy accumulation.
Heavily tortuous veins in the calf may require more energy, increasing the risk of damage to surrounding tissues, postoperative thrombosis, swelling, pain, and phlebitis. In such cases, EVLT alone may not suffice. To overcome this, we combined EVLT with vein stripping.
Drawing from traditional surgical practices, we introduced a tourniquet during EVLT:
Procedure: After completing EVLT, the affected limb is elevated for 1–2 minutes, a tourniquet is applied (not on the calf), and stripping is performed.
Purpose: The tourniquet minimizes bleeding and aids vein removal without increasing the risk of thrombus migration to deep veins.
EVLT is a highly effective, minimally invasive treatment for varicose veins. However, complications such as burns, phlebitis, recurrence, and pain can arise from improper technique. Through refined approaches, such as combining EVLT with high ligation, careful energy management, and the use of adjunct methods like saline spraying and tourniquet application, we have significantly reduced complication rates while preserving therapeutic efficacy.


Based on 7721 Recommendations | Rated 4.68 Out of 5
Happy Patients
Clinics
Cities
Surgeries
Doctors
Hospitals
Heal painful anal fissures with advanced, non-surgical care.
Quick relief, minimal downtime, expert proctology support…
Treat anal fistula with safe, advanced procedures.
Minimally invasive care with faster recovery.

A varicocele is an enlargement of the veins within the scrotum, similar to varicose veins, often causing pain or fertility issues.
Heal painful anal fissures with advanced, non-surgical care.
Quick relief, minimal downtime, expert proctology support…

Treatments include lifestyle changes, compression stockings, laser therapy, sclerotherapy, and minimally invasive surgeries like laser or radiofrequency ablation.
With advanced laser or radiofrequency treatments, recurrence is very low, but maintaining a healthy lifestyle helps prevent new varicose veins from forming.
If you have severe pain, swelling, skin changes, bleeding veins, or ulcers, your doctor may recommend surgical or laser treatment for long-term relief.
Yes, laser treatment is a safe, minimally invasive procedure with quick recovery, less pain, and lower chances of recurrence compared to traditional surgery.
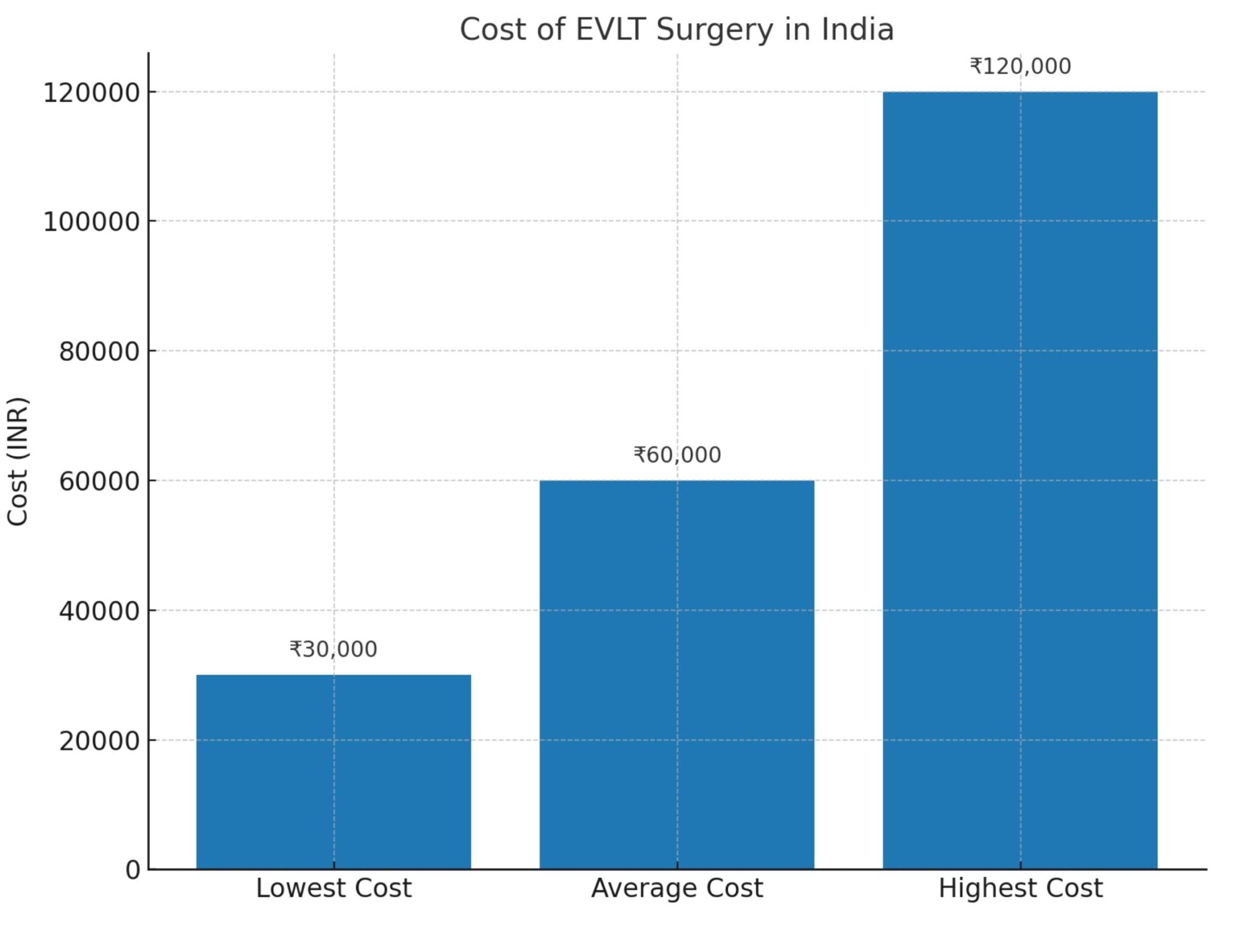
varicose veins laser surgery cost in Vizag ● low-cost varicose veins surgery in Hyderabad ● cashless varicose veins treatment near me ● painless varicose veins surgery in Vijayawada ● varicose veins treatment with insurance in Vizag ● varicose veins removal surgery cost in Hyderabad ● varicose veins operation packages in Vijayawada ● affordable varicose veins treatment near me ● varicose veins laser treatment clinic in Hyderabad ● varicose veins doctor consultation charges in Vizag ● best varicose veins surgery cost in Vijayawada ● varicose veins treatment hospital near me ● varicose veins laser operation price in Hyderabad ● low-cost varicose veins laser treatment in Vizag ● varicose veins removal cost near me ● varicose veins treatment with EMI in Vijayawada ● varicose veins surgery specialist near me ● varicose veins surgery packages in Hyderabad ● varicose veins treatment clinic near me ● varicose veins laser surgery near me
Disclaimer: **The result and experience may vary from patient to patient.. ***By submitting the form or calling, you agree to receive important updates and marketing communications.
Getting an accurate diagnosis can be one of the most impactful experiences that you can have.

cure with care
Copyright © 2025. All rights reserved.
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
Happy Patients
Hospitals
Cities