The ulcers on your foot that are not healing can be a sign of diabetic foot ulcers. Reach out to an experienced vascular surgeon and get safe and advanced diabetic foot ulcer treatment as soon as possible to avoid possible complications. Book your appointment today with the best vascular surgeon.
Happy Patients
Disease
Hospitals
Cities
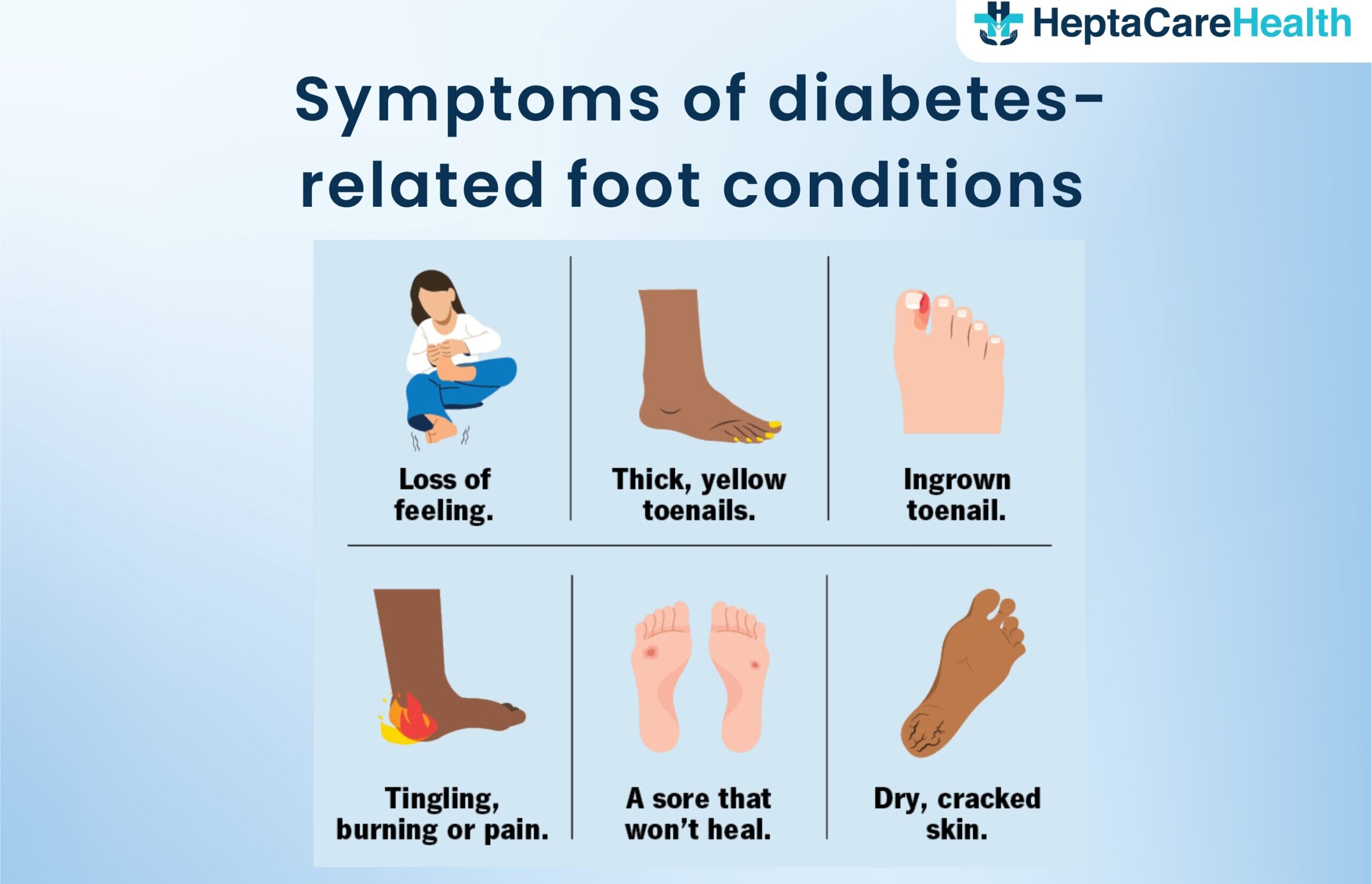
A diabetic foot ulcer is a medical condition in which the patient suffering from diabetes develops wounds in the foot which further grows to be an ulcer due to lack of proper blood circulation in the affected area. When a person with diabetes develops a foot injury, such as a blister, cut, or sore, they may not be aware of it due to the loss of sensation. The injury can go unnoticed and untreated, leading to the formation of a diabetic foot ulcer. If left untreated, diabetic foot ulcers can become infected and may lead to serious complications, such as skin infection, bone infection, or tissue death.
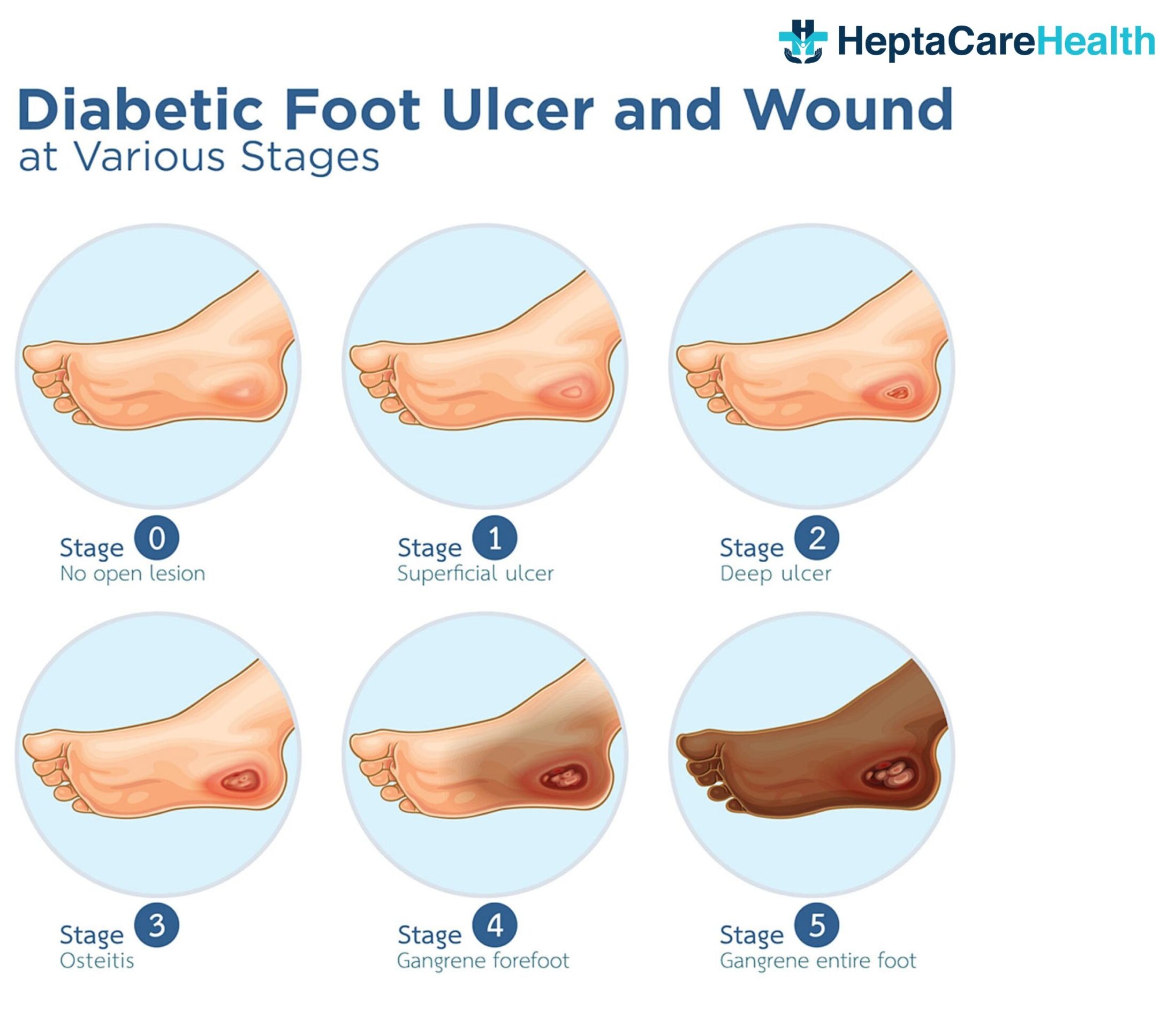
Diabetic foot ulcers are a serious complication of diabetes, often starting with a seemingly minor injury that can worsen rapidly due to nerve damage and poor blood flow circulation. While the initial symptoms like swelling, itching, and burning might seem manageable, neglecting these ulcers can lead to severe consequences. Here are a few types of diabetic foot ulcers that must be considered while taking treatment:
Early detection and proper management are crucial to prevent diabetic foot ulcers from progressing and having any severe complications. Regular foot checks, proper footwear, and maintaining good blood sugar control are essential steps in keeping your feet healthy. Remember, even a small injury can have serious consequences for diabetic feet, so don’t hesitate to seek medical attention if you notice any changes.
Before embarking on the journey of treatment for diabetic foot ulcers, a thorough diagnosis is performed by the doctor to assess the overall health of the patient. This diagnostic phase helps pave the way for a personalized treatment plan with the best chance of success.
Here are some of the tests mentioned that a doctor may perform to evaluate the patient’s health:
The treatment of diabetic foot ulcers generally involves a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals to guide the patient properly with the treatment procedures. The specific treatment options depend on the severity and characteristics of the ulcer, for a better and permanent cure, the doctor always advises surgical intervention, but the patient can always try the conservative methods prior.
Here are some of the common treatment options for diabetic foot ulcer:
It is important to note that the treatment approach may vary depending on individual circumstances, and a healthcare professional should be consulted for proper evaluation and management of diabetic foot ulcers.
Before undergoing Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment, several important preparations need to be made. Here are some key considerations:
During Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment, the specific procedures performed will depend on the characteristics and severity of the ulcer, as well as the individual patient’s condition. Here are some common surgical interventions that may be performed:
The benefits of diabetic foot ulcer treatment are numerous and significant. Prompt and effective treatment can help improve the healing process, prevent complications, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals with diabetic foot ulcers. Here are some specific benefits of diabetic foot ulcer treatment:
It is important for individuals with diabetic foot ulcers to seek early and appropriate treatment from healthcare professionals experienced in managing diabetic foot complications. Timely intervention and a comprehensive treatment approach can maximize the benefits and improve outcomes for individuals with diabetic foot ulcers.
While diabetic foot ulcer treatment aims to promote healing and prevent complications, there can be potential complications and side effects associated with the treatment.
It is important to note that not all individuals will experience these complications or side effects, and proper management and adherence to treatment plans can help minimize their occurrence. Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals and open communication with the care team is essential to address any concerns and manage complications effectively.
The recovery process of a diabetic foot ulcer can vary depending on the severity of the ulcer, the individual’s overall health, and the effectiveness of the treatment. Here are some general steps and considerations involved in the recovery process after treatment:
The recovery process can take weeks to months, depending on the size and depth of the ulcer. It is important to note that each individual’s situation is unique, and the recovery process may differ. Close collaboration with the vascular surgeon and adherence to their recommendations are crucial for optimal healing and minimizing the risk of complications or ulcer recurrence.
The cost of diabetic foot ulcer treatment in India ranges from Rs. <minCost> to Rs. <maxCost>. However, it is only an estimated cost range that varies for each patient, depending primarily on the diabetic foot ulcer stage. Additional key factors that influence the cost of treatment are listed below:
The overall cost of treatment is calculated based on the above-listed factors. The good thing is that diabetic foot ulcer treatment is covered under insurance as it is a critical condition. The treatment is deemed a medical necessity. Thus, patients only need to file a claim request to acquire authorization, and the insurance company will cover the expenses entirely or partially as specified in the policy.


Based on 7721 Recommendations | Rated 4.68 Out of 5
Happy Patients
Clinics
Cities
Surgeries
Doctors
Hospitals
Get relief from painful proctology with advanced laser treatment.
Minimally invasive, no stitches, same-day discharge…
Heal painful anal fissures with advanced, non-surgical care.
Quick relief, minimal downtime, expert proctology support…
Treat anal fistula with safe, advanced procedures.
Minimally invasive care with faster recovery.

Treatments include lifestyle changes, compression stockings, laser therapy, sclerotherapy, and minimally invasive surgeries like laser or radiofrequency ablation.
With advanced laser or radiofrequency treatments, recurrence is very low, but maintaining a healthy lifestyle helps prevent new varicose veins from forming.
If you have severe pain, swelling, skin changes, bleeding veins, or ulcers, your doctor may recommend surgical or laser treatment for long-term relief.
Yes, laser treatment is a safe, minimally invasive procedure with quick recovery, less pain, and lower chances of recurrence compared to traditional surgery.
varicose veins laser surgery cost in Vizag ● low-cost varicose veins surgery in Hyderabad ● cashless varicose veins treatment near me ● painless varicose veins surgery in Vijayawada ● varicose veins treatment with insurance in Vizag ● varicose veins removal surgery cost in Hyderabad ● varicose veins operation packages in Vijayawada ● affordable varicose veins treatment near me ● varicose veins laser treatment clinic in Hyderabad ● varicose veins doctor consultation charges in Vizag ● best varicose veins surgery cost in Vijayawada ● varicose veins treatment hospital near me ● varicose veins laser operation price in Hyderabad ● low-cost varicose veins laser treatment in Vizag ● varicose veins removal cost near me ● varicose veins treatment with EMI in Vijayawada ● varicose veins surgery specialist near me ● varicose veins surgery packages in Hyderabad ● varicose veins treatment clinic near me ● varicose veins laser surgery near me
Disclaimer: **The result and experience may vary from patient to patient.. ***By submitting the form or calling, you agree to receive important updates and marketing communications.
Getting an accurate diagnosis can be one of the most impactful experiences that you can have.

cure with care
Copyright © 2025. All rights reserved.
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
Happy Patients
Hospitals
Cities